Carbon markets are trading systems where carbon credits are bought and sold. There are two types of market:
Compliance markets are regulated by international, national or regional policy agreements. They are designed to progressively limit total carbon emissions in key sectors by two mechanisms – the ‘cap’: allocating businesses an increasingly strict annual quota for carbon emissions; and the ‘trade’: a trading market for businesses that emit more than their quota to purchase carbon credits from those that emit less, enabling the economy-wide target to be met.
Voluntary carbon markets where individuals or businesses can voluntarily trade carbon credits to compensate for their carbon footprint or meet corporate sustainability targets. They provide an important source of private climate finance, particularly in supporting investment in less developed countries.
To function, these markets need to have clear and transparent rules, governing bodies and buyers and sellers. Compliance markets are governed by national and international regulations and define the market participants – the buyers and sellers – through the regulation, usually large businesses from high-emission industries.
Voluntary markets are not regulated, but are organised with transparent rules, independent audit and verification/validation bodies and publicly accessible databases of projects and transactions. Voluntary markets typically rely on international standards to enhance integrity, such as ISO 14064 and government approved data and principles for carbon assessment.
Buyers enter the voluntary market to meet personal carbon compensation targets or to comply with corporate, investor or industry standards in sustainability. Voluntary carbon credits are produced by projects seeking to develop revenue streams through the credits. These credits can be traded on the market and are ultimately retired on behalf of the end-user and a public retirement certificate is issued.
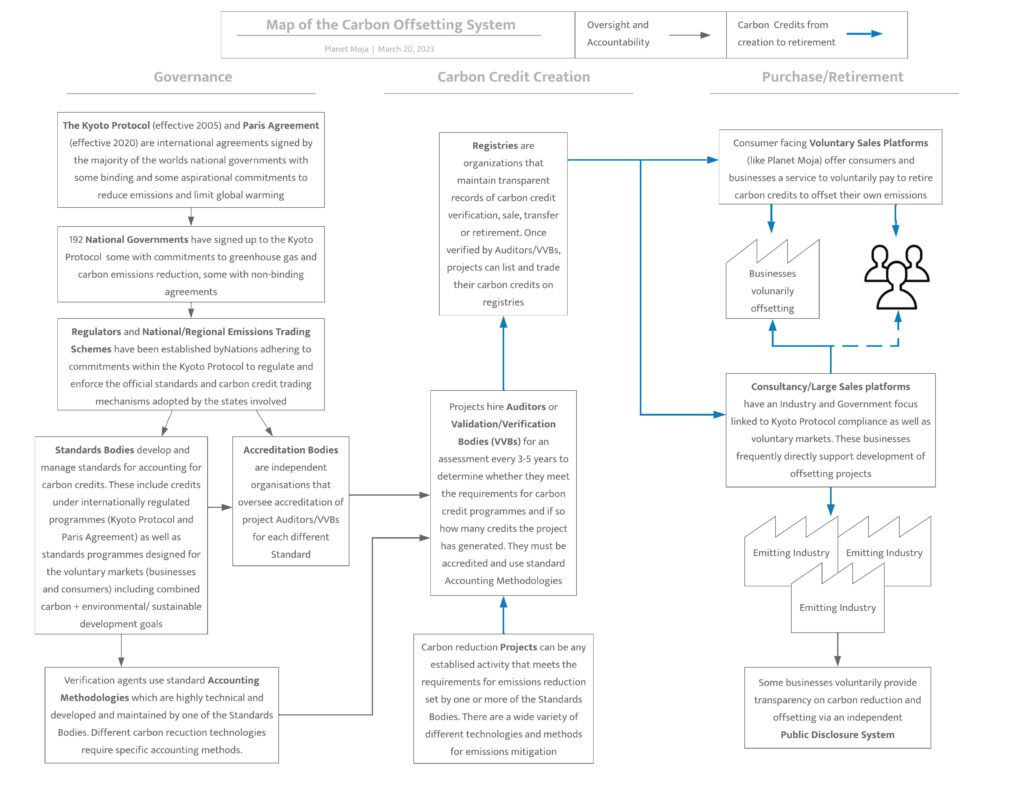
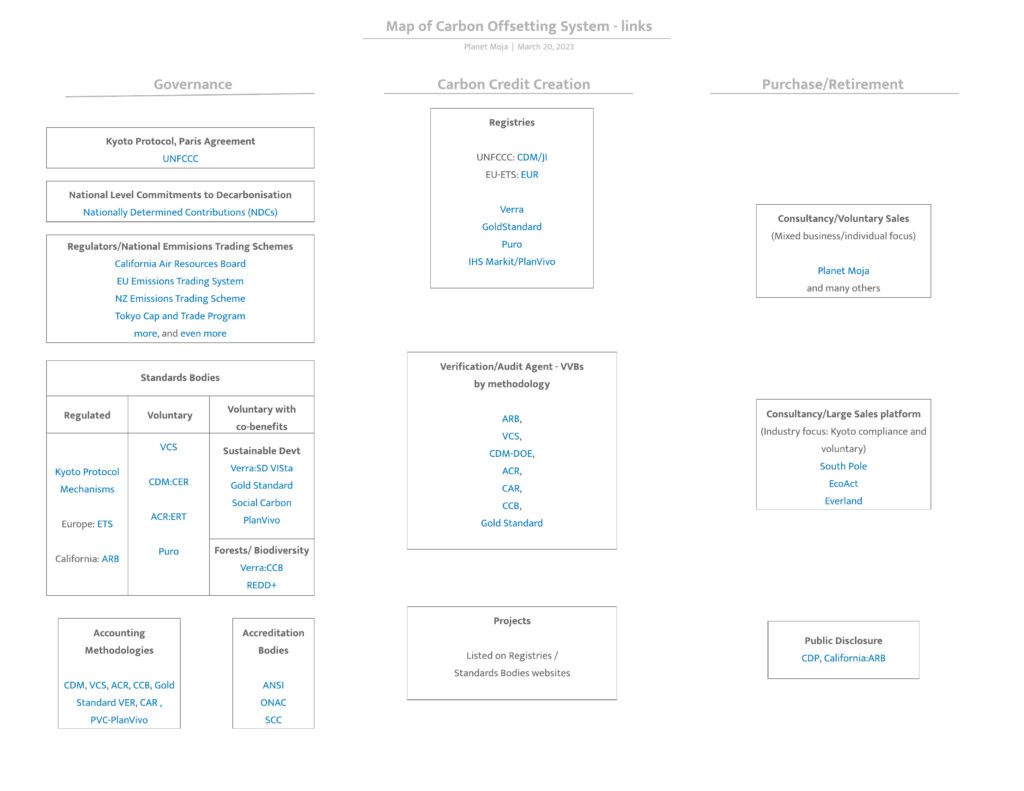
The first diagram below gives an overview of the governance, the credit creation process and the purchase and retirement process. The second diagram provides links to example organisations across the carbon market system.